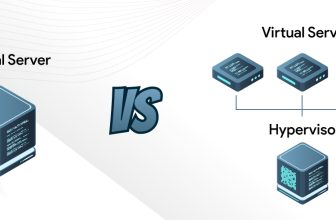
What is Server Virtualization?

In this server-dependent world, virtualization is obviously a hot topic. With multiple innovations, advancements, and trends in the IT world, going virtual not only simplifies the work process to a great extent but also allows you to experiment working with multiple operating systems. Let’s go a little deeper into this server virtualization.
Definition and Analogy
The process of creating numerous virtual machines from one physical server host using virtualization software is called server virtualization. Entire server hardware is shared between the virtual machines giving them the ability to think, work, and become an individual server system.
Consider this carpooling analogy. A student going to college, a professor attending a conference, and an employee trying to make it to the office on time carpool a cab. All three of them share equal amounts of space and comfort while reaching their destination. In an event that the car breaks down, they can switch to another cab without waiting for the former cab to get repaired. This is exactly how server virtualization works.
Server Virtualization Software
Server virtualization software reduces the dependency of physical hardware for using various operating systems. It uses hypervisors to carry out the task.
These hypervisors are also called virtual machine monitors (VMMs) and are basically of two types.
Type 1 – that can be installed directly on the server.
Type 2 – that is installed on the top of the server’s OS.
The server virtualization software is solely responsible for centrally controlling and optimizing all the virtual machines’ environments.
Why Use Server Virtualization?
Now that you know how server virtualization works and what helps it work, the next important question is why? This is a little briefing about that.
Firstly, the under-utilized and over-utilized server hardware is always a loss that has to be compensated in one way or another. But, server virtualization eradicates this problem. Another important reason to go for server virtualization is that you gain the flexibility to work on multiple operating systems with the resources of a single server. You might think that you can simply buy another server for a separate OS, but that is such a waste of money and resources. With server virtualization, you can run multiple operating systems isolated from one another by utilizing all your server hardware capacity and perform your workflows without compromising on the work quality.
Types of Server Virtualization
There are three types of server virtualization that serve users in their own ways. In each of them, the physical server remains as the host. They are categorized depending on their isolation behavior.
- Full virtualization model
This is also called the virtual machine model. In this server virtualization type, virtual machines are completely unaware of the existence of hypervisors. The virtual machines consider themselves extremely efficient and run independently by utilizing the host server hardware but are completely isolated from the host. - Paravirtual model
In the paravirtual machine model, the VM servers are completely aware of the hypervisor’s existence. The virtual machines, hypervisor, and the host work as a well-integrated unit. In this model, the operating systems communicate with the hypervisors through hypercalls. Hypercalls are nothing but small comments passed between OS and paravirtual hypervisor. - OS-level virtualization
Every host OS has some virtualization capability as a part of it. In the OS-level virtualization, this part of the host OS carries out the tasks of a fully virtualized hypervisor. This type of virtualization is called containerization, and it creates a homogenous environment. This means that the host server and virtual servers must run on the same OS. This is more efficient and faster to launch than other versions.
Which Method is The Best?
The answer to this question relies on the administrator’s requisites. OS-level virtualization is the best choice for those whose physical servers work on the same OS. If users plan on working with multiple operating systems, then the paravirtual model stands a better chance. This method is still new, and most companies use full virtualization for fulfilling multiple OS needs. But, the need for the paravirtual model might escalate in the future.
Advantages of Server Virtualization
Server virtualization comes with a bunch of advantages that can persuade users to choose virtualization among any other included options. These advantages include,
- Minimized capital
Virtualization converts your single server into multiple credible servers that help in minimizing the capital and maintenance costs when in need of multiple OS or servers. It allows you to perform your workflows uninterruptedly with basic investments. - Improved resource utilization
With server virtualization, you don’t have to worry about your server resources being wasted. You can run different OS-based applications using the same physical server resources. - Saves your time
With fewer servers, it is given that you spend less time maintaining and more time progressing. Time consuming tasks such as backups, audits, recovery, etc can be done in less time than expected. - Reduced energy consumption
Servers require more power to run and much more for cooling down. The concept of server virtualization reduces the physical server usage and significantly reduces the energy consumed as well. - Eliminated downtime
There is no scope of downtime in server virtualization as you can easily switch from one server to another. This increases the availability, efficiency, productivity, and responsiveness of your workflows. - Greater disaster recovery
Server virtualization evidently makes it easier to recover your data after any unexpected disasters. Users can create a replication site on virtual machines or test disaster recovery methods beforehand to avoid data losses. - Faster application provisioning
Most of the new applications require a new server, and their setup consumes a lot of time. But, with the server virtualization, application provisioning and deployment are done fastly as there is no need to set up a new server.
Disadvantages of Server Virtualization
The advantages of server virtualization are so promising the people often overlook the limitations it comes along with. These are the prominent server virtualization drawbacks.
- Dependency
The entire virtual environment is completely dependent on the host server. This dependency can be a disadvantage because a simple issue with the host server can affect the functioning of the virtual machines. - Limited resource availability
Applications that demand excessive storage and processing power should only be installed if the host server has abundant resources left, otherwise, the system slows down and makes it impossible even to carry out simple tasks. Also, too many virtual machines can impact the overall processing power. - Performance uncertainty
When multiple virtual machines run on the same server, it becomes impossible to determine and maintain the performance of each virtual machine. - Maintenance & monitoring
Virtual machines are likely to be attacked easily. So you have to constantly monitor the VM workflows and maintain security systems regularly. - Complexity
Server virtualization has a fair share of complexity. It requires numerous links to work cohesively. Physical access for USB cards, specific drives, etc might be a little tricky and should be done carefully.
Final Takeaway
Server virtualization is an amazing concept that could save hours of toil if utilized properly. Multiple companies and organizations choose this server virtualization despite their disadvantages. Bigger, better, and efficient progress can be achieved with little investment of time and money with this server virtualization. The complete potential of this amazing concept is yet to be witnessed!